Title: Navigating the Complexities of the Global Economy
Introduction:
The global economy is an intricate web of interconnected financial systems, trade networks, and economic policies that shape the lives of people across the globe. It is a dynamic entity, constantly evolving and responding to various factors such as technological advancements, geopolitical developments, and socio-economic trends. In this article, we will explore some key aspects of the global economy and shed light on its complexities.
Interdependence:
One fundamental characteristic of the global economy is interdependence. Nations rely on each other for resources, markets, and investment opportunities. A change in one country’s economic condition can have ripple effects that reverberate across borders. For instance, a slowdown in one major economy can impact commodity prices worldwide or disrupt supply chains on a global scale.
Trade and Globalization:
Trade plays a vital role in the global economy. The exchange of goods and services between nations fosters economic growth and creates employment opportunities. Over the years, globalization has accelerated this process by reducing barriers to trade through agreements like free trade agreements (FTAs) or regional trade blocs like the European Union.
Emerging Markets:
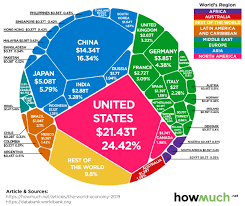
Emerging markets have become significant players in the global economy. Countries such as China, India, Brazil, and others have experienced rapid economic growth over recent decades. Their rise has shifted economic power away from traditional developed economies towards these emerging giants. This trend has implications for investment flows, consumption patterns, and market dynamics worldwide.
Financial Markets:
Financial markets are at the heart of the global economy. Stock exchanges, bond markets, currency markets, and other financial institutions facilitate capital flows between countries. These markets are influenced by various factors such as interest rates set by central banks, investor sentiment, political stability or instability in different regions.
Economic Policies:
Governments play a crucial role in shaping their respective economies through fiscal policies (taxation and public spending) and monetary policies (interest rates and money supply). These policies aim to manage inflation, stimulate economic growth, and maintain stability. However, striking the right balance is a complex task, as decisions made by one country can have spillover effects on others.
Inequality and Sustainability:
The global economy also faces challenges related to inequality and sustainability. While economic growth has lifted millions out of poverty, there are still significant disparities within and between nations. Addressing income inequality, ensuring access to basic services, and promoting sustainable development are critical for long-term stability and prosperity.
Conclusion:
Understanding the complexities of the global economy is essential for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike. It requires a holistic approach that considers the interplay between various factors affecting economies worldwide. As we navigate an increasingly interconnected world, it is crucial to foster cooperation, promote inclusive growth, and strive for sustainable economic practices that benefit all nations.
Advantages of Global Economy: Enhancing Interconnectivity, Expanding Markets, Lowering Costs, Advancing Technology, Boosting Competition, Creating Jobs, Offering Investment Opportunities, Broadening Consumer Choice, Elevating Living Standards
- Increased interconnectivity
- Expansion of markets
- Lower costs
- Improved technology
- Increased competition
- Job creation
- Investment opportunities
- Greater choice for consumers
- Improved standards of living
Challenges in the Global Economy: A Closer Look at 6 Cons
- Increased inequality between developed and developing countries
- Rising levels of debt within countries
- Imbalance of power between large multinational corporations and smaller businesses
- Volatility in currency markets due to speculation and political uncertainty
- Vulnerability to global economic shocks, such as pandemics or natural disasters
- Environmental degradation caused by unsustainable production practices
Increased interconnectivity
Increased Interconnectivity: Boosting Trade Efficiency through Globalization
Globalization has ushered in an era of increased interconnectivity among countries, revolutionizing the way trade is conducted. This pro of the global economy has paved the way for more efficient and effective international trade, benefiting businesses and consumers worldwide.
One of the primary advantages of increased interconnectivity is the ease with which goods and services can now be exchanged between nations. The advancements in transportation and communication technology have significantly reduced barriers to trade. Today, companies can seamlessly transport their products across borders, reaching new markets and expanding their customer base.
Furthermore, globalization has facilitated the development of global supply chains. Companies can now source raw materials, components, and expertise from various countries to create a final product. This interconnectedness allows businesses to capitalize on cost-effective production methods while maintaining high quality standards.
The increased interconnectivity also fosters competition among nations, leading to improved efficiency and innovation. Companies are motivated to enhance their productivity levels to stay competitive in a global market. This drive for efficiency ultimately benefits consumers by offering a wider range of products at competitive prices.
Moreover, globalization has opened up opportunities for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to participate in international trade. With reduced barriers and easier access to global markets, SMEs can now compete on a level playing field with larger corporations. This inclusivity promotes economic growth by stimulating entrepreneurship and job creation.
Additionally, increased interconnectivity has facilitated knowledge sharing across borders. Countries can learn from each other’s best practices, technological advancements, and innovative approaches to various industries. This exchange of ideas fuels progress and encourages collaboration between nations.
However, it is important to acknowledge that while increased interconnectivity brings numerous benefits, it also poses challenges that need careful consideration. Issues such as income inequality, environmental sustainability, and cultural preservation require attention as we navigate the complexities of a globalized world.
In conclusion, the increased interconnectivity brought about by globalization has revolutionized international trade. It has facilitated the efficient exchange of goods and services, fostered competition and innovation, and opened up opportunities for businesses of all sizes. Embracing this pro of the global economy can lead to greater economic prosperity and a more interconnected world.
Expansion of markets
Expansion of Markets: Globalisation’s Boon to Businesses
Globalisation has revolutionised the way businesses operate, opening up vast opportunities for growth and profit through the expansion of markets. With the global economy becoming more interconnected than ever before, companies can now access larger markets that were once out of reach. This pro of globalisation has undoubtedly transformed the business landscape and paved the way for unprecedented growth.
In the past, businesses were often confined to their domestic markets, with limited prospects for expansion. However, with the advent of globalisation, barriers to international trade have been significantly reduced, allowing companies to tap into new markets across borders. This newfound access to a broader customer base has provided businesses with a platform to showcase their products or services on a global scale.
Expanding into new markets brings several benefits for businesses. Firstly, it allows them to diversify their revenue streams and reduce dependence on a single market. By operating in multiple countries, companies can mitigate risks associated with economic downturns or fluctuations in specific regions. This diversification strategy helps safeguard against market-specific challenges and ensures a more stable business environment.
Moreover, accessing larger markets enables companies to benefit from economies of scale. With increased production volumes and higher sales potential, businesses can achieve cost efficiencies through bulk purchasing, streamlined manufacturing processes, and improved distribution networks. These cost savings can translate into higher profit margins and competitive pricing strategies that attract more customers.
The expansion of markets also fosters innovation and competition among businesses. When companies enter new territories, they are exposed to diverse consumer preferences and market dynamics. This exposure drives them to adapt their products or services to meet local demands or develop innovative solutions tailored specifically for different markets. In turn, this competition spurs continuous improvement and fosters creativity within industries.
Furthermore, entering new markets often requires collaboration with local partners or suppliers. These partnerships promote knowledge exchange and cultural understanding between different regions. Through such collaborations, businesses gain insights into local business practices, consumer behavior, and market trends. This cross-pollination of ideas and expertise can lead to enhanced business strategies and the development of new products or services that cater to a wider audience.
In conclusion, the expansion of markets made possible by globalisation has been a game-changer for businesses worldwide. It has provided unprecedented opportunities for growth and profit. By accessing larger markets, companies can diversify their revenue streams, achieve economies of scale, foster innovation, and collaborate with local partners. As the global economy continues to evolve, businesses must embrace these opportunities to stay competitive and thrive in an increasingly interconnected world.
Lower costs
Title: The Global Economy’s Pro: Lower Costs Boost Business Profitability
Introduction:
The global economy has brought about numerous advantages for businesses, and one significant benefit is the opportunity to lower costs. By tapping into cheaper labour and materials from other countries, companies can streamline their production processes, enhance efficiency, and ultimately increase profitability. In this article, we will delve into how accessing cost-effective resources on a global scale has become a game-changer for businesses.
Access to Cheaper Labour:
One of the primary ways the global economy benefits businesses is by providing access to a diverse pool of skilled labour at lower costs. Many developing countries offer highly educated and skilled workers who are willing to work for wages that are comparatively lower than those in developed nations. This allows businesses to reduce their labour expenses significantly while maintaining or even improving productivity levels.
Cost-Effective Materials:
In addition to cheaper labour, the global economy also enables businesses to source materials and components at more competitive prices. Certain regions may have abundant natural resources or specialized manufacturing capabilities that result in lower material costs. By accessing these resources through international trade networks, businesses can take advantage of cost-effective inputs, reducing their overall production expenses.
Economies of Scale:
The global economy facilitates economies of scale by enabling businesses to expand their markets beyond national boundaries. With larger customer bases, companies can increase their production volumes, leading to reduced per-unit costs through bulk purchasing and streamlined manufacturing processes. This allows them to achieve higher profit margins while remaining competitive in the global marketplace.
Enhanced Competitiveness:
Lowering costs through global economic integration enhances a company’s competitiveness in multiple ways. Firstly, reduced production costs allow businesses to offer products or services at more affordable prices compared to competitors who operate solely within domestic markets. Secondly, increased profitability resulting from cost savings can be reinvested in research and development, innovation, or marketing efforts, further strengthening a company’s competitive advantage.
Job Creation and Economic Growth:
Lower production costs can also lead to increased job creation and economic growth. By reducing expenses, businesses can allocate resources towards expanding operations, opening up new facilities, or investing in technology. These activities generate employment opportunities both domestically and internationally, contributing to overall economic development.
Conclusion:
The global economy has revolutionized the business landscape by providing access to lower-cost labour and materials from around the world. This advantage allows companies to reduce production costs, increase profitability, enhance competitiveness, and foster economic growth. However, it is important to ensure that these benefits are accompanied by fair trade practices and responsible business conduct to promote sustainable development for all stakeholders involved in the global economy.
Improved technology
Improved Technology: Boosting Efficiency and Productivity in a Global Economy
In today’s interconnected world, one of the significant advantages of the global economy is the access to improved technology. Businesses can now tap into the latest innovations and advancements developed in other countries that may not be readily available locally. This opens up a world of possibilities, allowing companies to enhance their efficiency and productivity levels.
Technological progress knows no boundaries, and with the global economy, businesses can leverage cutting-edge tools, software, machinery, and processes from around the world. This cross-border exchange of technology enables companies to stay at the forefront of their industries and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
By embracing new technologies from abroad, businesses can streamline their operations, automate repetitive tasks, and optimize their production processes. For instance, advanced manufacturing techniques or robotics developed in one country can revolutionize production lines elsewhere. This leads to increased output levels while reducing costs and enhancing overall quality.
Moreover, improved technology enables businesses to reach new markets and expand their customer base globally. With digital platforms and e-commerce solutions becoming increasingly accessible worldwide, companies can tap into previously untapped markets with ease. This expansion not only drives revenue growth but also fosters economic development by creating job opportunities both locally and internationally.
The benefits of adopting foreign technologies are not limited to large corporations alone; small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) also stand to gain significantly. In a global economy where knowledge is shared across borders, SMEs can access cost-effective software solutions or cloud-based services that were once only available to larger enterprises. This levels the playing field for smaller businesses, enabling them to compete more effectively on a global scale.
However, it is important for businesses to adapt these technologies effectively by considering local contexts and requirements. Cultural factors or regulatory frameworks may necessitate customization or adaptation of foreign technologies to suit specific markets.
In conclusion, the improved technology made accessible through the global economy presents immense opportunities for businesses. By embracing innovations from around the world, companies can enhance their efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness. This not only benefits individual businesses but also contributes to overall economic growth and development. As technology continues to advance, the global economy will remain a catalyst for progress, driving innovation and enabling businesses to thrive in an increasingly interconnected world.
Increased competition
Title: The Global Economy’s Pro: Increased Competition for Consumer Benefit
Introduction:
In today’s interconnected world, the global economy has brought numerous advantages, one of which is increased competition. This article explores how the global economy fosters competition between companies on an international scale, ultimately leading to improved products and lower prices for consumers.
Competition Breeds Innovation:
The global economy creates an environment where businesses must constantly innovate to stay ahead. With access to a broader market, companies are compelled to develop new ideas, technologies, and strategies to differentiate themselves from their competitors. This drive for innovation leads to the creation of better products and services that meet the evolving needs and preferences of consumers.
Quality Improvements:
In a competitive global marketplace, companies strive to offer high-quality products and services in order to attract customers. To gain a competitive edge, businesses invest in research and development, ensuring that their offerings meet or exceed international standards. Consumers benefit from this commitment to quality as they gain access to superior goods that have undergone rigorous testing and refinement.
Lower Prices:
Increased competition often results in lower prices for consumers. When companies vie for market share on a global scale, they are compelled to optimize their production processes, reduce costs, and operate efficiently. As a result, they can offer their products at more competitive prices. Consumers benefit from this price reduction as it allows them greater purchasing power and access to a wider range of goods.
Product Diversity:
The global economy encourages companies to cater to diverse markets with varying needs and preferences. To succeed globally, businesses must adapt their products or create new ones tailored specifically for different regions or cultures. Consequently, consumers are presented with a wider array of choices as companies strive to meet the demands of various markets around the world.
Consumer Empowerment:
With increased competition comes greater consumer empowerment. Companies recognize that they must win over customers by providing exceptional value for money. As a result, consumers have more influence over businesses’ practices and offerings. They can compare products, read reviews, and make informed decisions based on their preferences, ultimately driving companies to continuously improve and deliver better experiences.
Conclusion:
The global economy’s pro of increased competition has significant benefits for consumers. It fosters innovation, drives quality improvements, lowers prices, offers product diversity, and empowers consumers with more choices. As companies compete on an international scale, consumers are the ultimate beneficiaries of this dynamic environment, enjoying access to better products at more affordable prices.
Job creation
Globalization has undoubtedly brought about numerous benefits to the global economy, and one significant advantage is job creation. As companies expand their operations internationally, they often seek out cheaper labor sources in other countries. This pursuit of cost-effectiveness and efficiency has led to the creation of new jobs worldwide.
In today’s interconnected world, businesses can tap into a diverse pool of talent and resources from various corners of the globe. They can establish production facilities or outsource certain tasks to regions where labor costs are lower, enabling them to produce goods or services at a reduced expense. This cost-saving measure allows companies to remain competitive in the global market.
By investing in countries with lower labor costs, companies not only benefit from reduced expenses but also contribute to local economies by providing employment opportunities. These newly created jobs can have a transformative impact on individuals and communities, lifting people out of poverty and improving their standard of living.
Moreover, job creation resulting from globalization is not limited to manufacturing industries alone. It extends across sectors such as information technology, customer service, finance, research and development, and more. This diversification offers a broader range of employment options for people with different skill sets and educational backgrounds.
The positive impact of job creation goes beyond economic growth; it also fosters social stability. When individuals have access to meaningful employment opportunities, they are more likely to feel empowered and engaged in society. This can lead to reduced inequality, increased social mobility, and improved overall well-being within communities.
However, it is important to acknowledge that globalization’s impact on job creation is not without challenges. It can lead to job displacement in certain sectors or regions where industries struggle to compete with cheaper alternatives abroad. Therefore, it becomes crucial for governments and policymakers to implement strategies that support workers through retraining programs or by fostering innovation in emerging industries.
In conclusion, one significant pro of the global economy is job creation resulting from globalization. By seeking out cheaper labor sources abroad, companies can produce goods or services more efficiently and cost-effectively. This expansion creates new employment opportunities, helps alleviate poverty, and contributes to social and economic development worldwide. However, it is essential to address the potential negative consequences of job displacement and ensure that workers are supported in transitioning to new opportunities.
Investment opportunities
Title: Global Economy Unleashes Investment Opportunities
Introduction:
In today’s interconnected world, the global economy offers a multitude of advantages to companies and investors. One significant benefit is the access to a wider range of investment options, thanks to globalization. This article explores how the global economy opens up new avenues for investment, providing companies with greater potential returns on their investments when managed effectively.
A World of Investment Possibilities:
Globalization has dismantled barriers to trade and investment, allowing companies to explore opportunities beyond their domestic markets. With advancements in technology and communication, businesses can now easily access information about international markets, industries, and emerging trends. This expanded reach enables them to consider a broader range of investment options across various sectors and geographical locations.
Diversification and Risk Management:
The global economy offers companies the chance to diversify their investment portfolios. By investing in different regions or industries, businesses can spread their risk and reduce vulnerability to local economic fluctuations or sector-specific challenges. Diversification helps protect investments from unforeseen events that may impact one particular market or industry, thus enhancing overall stability.
Emerging Markets as Growth Engines:
Globalization has propelled the rise of emerging markets as attractive investment destinations. These economies often experience rapid growth rates and present untapped potential for companies seeking higher returns on their investments. Countries such as China, India, Brazil, and others offer vast consumer markets and burgeoning middle-class populations that drive demand for goods and services.
Access to Specialized Expertise:
The global economy allows companies to tap into specialized expertise from around the world. By investing globally, businesses gain exposure to diverse talent pools with unique skills, knowledge, and innovative ideas. Collaborating with international partners or acquiring foreign firms provides access to cutting-edge technologies and best practices that can enhance competitiveness in both domestic and foreign markets.
Capitalizing on Comparative Advantages:
Globalization enables companies to leverage comparative advantages available in different regions. For example, a company based in a country with abundant natural resources may invest in countries with advanced manufacturing capabilities. By capitalizing on the strengths of different regions, companies can optimize production processes, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
Conclusion:
The global economy offers companies an array of investment opportunities that can lead to greater potential returns if managed correctly. By embracing globalization and expanding their investment horizons, businesses can diversify risk, tap into emerging markets, access specialized expertise, and capitalize on comparative advantages. However, it is crucial for companies to conduct thorough research, assess risks diligently, and adapt their strategies to navigate the complexities of the global marketplace effectively. With careful planning and execution, investment opportunities in the global economy can pave the way for long-term growth and success.
Greater choice for consumers
Title: Global Economy: Unlocking a World of Choice for Consumers
In today’s interconnected world, the global economy has revolutionized the way we consume. One significant advantage it brings is the greater choice available to consumers. With products from different parts of the world easily accessible, consumers now have an unprecedented array of options at their fingertips, leading to increased variety and competition.
The expansion of international trade has opened up new markets and connected producers and consumers across borders. This connectivity means that consumers can enjoy products that were once considered exotic or out of reach. From unique handicrafts to technological innovations, the global economy has made it possible for consumers to access a diverse range of goods from all corners of the globe.
This increased choice benefits consumers in multiple ways. Firstly, it allows individuals to explore and experience different cultures through their purchases. Whether it’s trying out traditional clothing from distant lands or indulging in international cuisine, consumers can embrace diversity and broaden their horizons without leaving their own neighborhoods.
Furthermore, a wider range of products fosters healthy competition among producers. As businesses strive to capture consumer attention in a crowded marketplace, they are compelled to innovate and improve their offerings continually. This competition drives down prices as companies vie for customers’ loyalty by offering better quality and more affordable options.
The availability of diverse products also empowers consumers with greater control over their purchasing decisions. They can compare prices, features, and reviews from around the world before making informed choices that best suit their needs and preferences. The ability to access a global marketplace means that consumers are no longer limited by what is locally available but can seek out precisely what they desire.
However, it is important to note that while global trade increases consumer choice, it also poses challenges such as sustainability concerns and ethical considerations regarding production practices. It is crucial for both businesses and consumers to prioritize responsible consumption by supporting sustainable practices and ensuring fair treatment throughout supply chains.
In conclusion, the global economy has undeniably expanded consumer choice in remarkable ways. It has broken down barriers, allowing consumers to explore a world of products and experiences previously unimaginable. By embracing this diversity, consumers can find products that align with their values and enjoy the benefits of healthy competition that drives down prices. With responsible choices, we can harness the power of the global economy to create a more vibrant and inclusive marketplace for all.
Improved standards of living
Improved Standards of Living: The Global Economy’s Positive Impact
The global economy has brought about significant improvements in standards of living worldwide, positively impacting millions of lives. This pro of the global economy can be attributed to several factors, including job creation, increased trade opportunities, and improved access to essential goods and services.
One of the key ways the global economy has contributed to improved standards of living is through job creation. As businesses expand their operations across borders, they create employment opportunities for people in various countries. This not only reduces unemployment rates but also enables individuals to earn a livelihood and support their families. Access to stable employment leads to increased income levels, allowing individuals to afford better housing, education, healthcare, and other basic necessities.
Furthermore, the global economy has facilitated increased trade between nations. Through trade agreements and globalization, countries have been able to tap into new markets and diversify their sources of revenue. This expansion in international trade has led to economic growth and prosperity for many nations. Increased trade also allows for the exchange of goods at competitive prices, ensuring that consumers have access to a wider range of products.
Another significant benefit is the improved access to essential goods like food, medicine, clothing, and more. Global supply chains ensure that these commodities can reach even the most remote areas around the world. This accessibility helps combat poverty by providing individuals with vital resources that contribute to their overall well-being.
Moreover, advancements in technology and communication have played a crucial role in enhancing standards of living globally. The digital revolution has connected people across continents and facilitated knowledge-sharing and innovation. It has opened up avenues for education and skill development through online platforms, empowering individuals with greater opportunities for personal growth and economic advancement.
While acknowledging these positive aspects of the global economy’s impact on standards of living, it is important to address any potential negative consequences such as income inequality or environmental concerns. Striving for inclusive growth that benefits all segments of society remains a priority.
In conclusion, the global economy has played a vital role in reducing poverty levels and improving standards of living worldwide. By creating jobs, increasing trade, and ensuring access to essential goods and services, it has enabled individuals to lead more fulfilling lives. However, it is crucial to continue working towards sustainable and equitable economic practices that benefit all members of society.
Increased inequality between developed and developing countries
Title: The Conundrum of Increased Inequality in the Global Economy
Introduction:
As the global economy continues to expand, one of the significant downsides is the widening gap between developed and developing countries. This growing inequality poses numerous challenges for both the global community and individual nations. In this article, we will explore how increased inequality between developed and developing countries can hinder progress and perpetuate socio-economic disparities.
The Divide Widens:
Globalization has undoubtedly brought economic benefits to many nations, but it has also exacerbated existing inequalities. Developed countries, with their advanced infrastructure, technology, and skilled workforce, have been able to leverage these advantages to achieve robust economic growth. Meanwhile, developing countries often struggle to compete on a level playing field due to limited resources, inadequate infrastructure, and technological gaps.
Trade Imbalances:
One of the key drivers of inequality is trade imbalances between developed and developing nations. Developed economies often dominate global markets with their established industries and strong export capabilities. This can lead to unequal exchange relationships where developing countries primarily serve as suppliers of raw materials or low-value goods. As a result, they face challenges in diversifying their economies and capturing a larger share of global value chains.
Limited Access to Capital:
Access to capital is vital for economic growth and development. However, developing countries often face barriers in accessing affordable financing due to higher perceived risks by lenders or limited financial infrastructure. This lack of capital restricts their ability to invest in critical sectors such as education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and technology adoption – all necessary components for sustainable economic growth.
Brain Drain:
Another consequence of increased inequality is brain drain – the migration of skilled professionals from developing countries to more developed nations. The allure of better opportunities abroad often leads highly educated individuals from developing countries seeking better prospects elsewhere. This loss of talent further hampers the development potential of these countries by depleting their human capital.
Social Implications:
Increased inequality can have severe social implications within both developed and developing countries. Inequality often leads to social unrest, political instability, and a sense of marginalization among disadvantaged populations. This can hinder social cohesion, impede progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and perpetuate cycles of poverty and exclusion.
Addressing the Challenge:
Tackling the issue of increased inequality between developed and developing countries requires a multi-faceted approach. Developed nations can play a role by promoting fair trade practices, providing development aid, and supporting capacity-building initiatives in developing countries. Additionally, investing in education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and technology transfer can help bridge the gap.
On the other hand, developing countries should focus on implementing sound economic policies that promote inclusive growth, reduce corruption, and foster innovation. Encouraging entrepreneurship and diversifying their economies can also help create more opportunities for their citizens.
Conclusion:
The increased inequality between developed and developing countries is a pressing challenge that requires global attention and collaborative efforts. By addressing this issue head-on through equitable trade practices, targeted investments in human capital development, and inclusive economic policies, we can strive towards a more balanced global economy that benefits all nations. Only by narrowing this gap can we truly achieve sustainable development for everyone on our planet.
Rising levels of debt within countries
Title: The Burden of Rising Debt Levels in the Global Economy
Introduction:
As the global economy continues to evolve, one concerning con that has gained prominence in recent years is the escalating levels of debt within countries. Mounting debt burdens pose significant challenges for both developed and developing nations, with potential consequences that extend far beyond their borders. In this article, we will explore the implications of rising debt levels and shed light on why it is a cause for concern.
The Debt Trap:
One of the primary concerns associated with increasing debt levels is the risk of falling into a debt trap. Governments often resort to borrowing to finance infrastructure projects, social programs, or to stimulate economic growth. However, if not managed prudently, excessive borrowing can lead to a situation where countries struggle to meet their debt obligations, resulting in a vicious cycle of borrowing more just to service existing debts.
Reduced Fiscal Flexibility:
High levels of debt limit a government’s ability to respond effectively during times of economic downturns or crises. When a significant portion of national income is allocated towards servicing debt payments, it leaves less room for investment in critical sectors such as healthcare, education, infrastructure development, and social welfare programs. This reduced fiscal flexibility can hinder long-term economic growth and exacerbate socio-economic inequalities.
Dependency on Foreign Creditors:
Many countries rely on foreign creditors to finance their debts. This dependence can create vulnerabilities as changes in global economic conditions or shifts in investor sentiment can lead to sudden increases in borrowing costs or limited access to credit. Such situations can severely hamper a country’s ability to manage its economy independently and may result in increased financial instability.
Inter-generational Burden:
Rising debt levels also impose an inter-generational burden. As governments accumulate more debt, future generations may be left grappling with the consequences – higher taxes, reduced public services, and limited economic opportunities. This can hinder social mobility and create an unfair burden on the youth who inherit the debts incurred by previous generations.
Global Economic Stability:
The interconnectedness of the global economy means that rising debt levels in one country can have spillover effects on others. Financial contagion, market volatility, and reduced investor confidence can spread rapidly across borders, leading to economic instability on a global scale. As seen during past financial crises, a domino effect can occur when heavily indebted countries struggle to meet their obligations, triggering a chain reaction that impacts the entire global economy.
Conclusion:
While debt can be a useful tool for governments to stimulate growth and address socio-economic challenges, rising levels of debt within countries present significant risks. It is imperative for governments to exercise prudence in managing their debts, focusing on sustainable fiscal policies and effective debt management strategies. By doing so, nations can mitigate the potential negative consequences of excessive borrowing and ensure long-term economic stability for their citizens and the global community as a whole.
Imbalance of power between large multinational corporations and smaller businesses
Title: The Imbalance of Power in the Global Economy: A Concern for Smaller Businesses
Introduction:
In the vast landscape of the global economy, a significant concern arises from the growing imbalance of power between large multinational corporations and smaller businesses. This article delves into this issue, highlighting the challenges faced by smaller enterprises and the potential consequences for economies worldwide.
The Dominance of Multinational Corporations:
Large multinational corporations wield immense influence in today’s global economy. With substantial financial resources, extensive networks, and significant market share, these corporate giants often enjoy advantages that smaller businesses struggle to match. Their ability to leverage economies of scale, negotiate favorable trade deals, and access global markets gives them a competitive edge.
Challenges Faced by Smaller Businesses:
Smaller businesses face numerous hurdles when operating in an environment dominated by multinational corporations. Limited access to capital and resources can hamper their growth prospects. Moreover, they often lack the bargaining power to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers or secure advantageous contracts with larger customers. This disadvantage can hinder their ability to compete effectively on both domestic and international fronts.
Unequal Market Competition:
The imbalance of power between large corporations and smaller businesses can result in unequal market competition. Multinational corporations may engage in predatory pricing or anti-competitive practices that stifle competition and limit opportunities for smaller players. This can lead to reduced innovation, limited consumer choice, and potentially higher prices.
Impact on Local Economies:
The dominance of multinational corporations can have adverse effects on local economies. Small businesses are often significant contributors to local employment, community development, and economic diversity. When these enterprises struggle or are forced out of business due to unfair competition or unfavorable market conditions, it can lead to job losses and a decline in overall economic vitality.
Addressing the Imbalance:
Efforts must be made at various levels to address this imbalance of power between large multinational corporations and smaller businesses:
- Regulatory Measures: Governments can enact and enforce regulations that promote fair competition, prevent monopolistic practices, and protect the interests of smaller businesses.
- Supportive Policies: Governments should implement policies that provide targeted support to small businesses, including access to finance, training programs, and assistance with market entry.
- Collaboration and Networking: Smaller businesses can benefit from forming alliances, networks, or industry associations to enhance their collective bargaining power and share resources.
- Consumer Awareness: Educating consumers about the importance of supporting local businesses can help level the playing field by encouraging conscious purchasing decisions.
Conclusion:
The imbalance of power between large multinational corporations and smaller businesses in the global economy presents a significant challenge. It is crucial for policymakers, business leaders, and consumers to recognize this issue and work towards creating a more equitable environment. By fostering fair competition and supporting smaller enterprises, we can promote economic diversity, innovation, and sustainable growth for the benefit of all stakeholders involved.
Volatility in currency markets due to speculation and political uncertainty
Title: The Perils of Volatility in Currency Markets: Speculation and Political Uncertainty
Introduction:
The global economy is not without its drawbacks, and one significant con that plagues currency markets is the volatility caused by speculation and political uncertainty. Fluctuations in exchange rates can have far-reaching consequences for businesses, investors, and even everyday consumers. In this article, we delve into the challenges posed by such volatility and its impact on the global economy.
Volatility in Currency Markets:
Currency markets are highly sensitive to speculation and political uncertainties. Speculators, driven by profit motives, engage in buying or selling currencies based on their predictions of future price movements. These speculative activities can introduce considerable volatility into currency markets, leading to rapid fluctuations in exchange rates.
Political Uncertainty:
Political events such as elections, policy changes, or geopolitical tensions can create significant uncertainty in currency markets. Investors often react to these events by adjusting their portfolios or hedging against potential risks. As a result, currency values can experience sudden swings as market participants respond to changing political landscapes.
Impact on Businesses:
Volatility in currency markets poses challenges for businesses engaged in international trade. Fluctuating exchange rates make it difficult to forecast costs accurately or plan long-term investments. For exporters and importers, sudden changes in currency values can significantly impact profitability. Moreover, companies operating across borders may face increased financial risk due to fluctuating exchange rates.
Investor Sentiment:
Currency market volatility also affects investor sentiment and capital flows. When uncertainty prevails, investors may become more cautious or risk-averse. This can lead to reduced investments in certain regions or currencies perceived as unstable, further exacerbating the volatility.
Consumer Purchasing Power:
Fluctuations in exchange rates directly impact consumer purchasing power when it comes to imported goods and services. A weakening domestic currency makes imports more expensive, potentially leading to higher prices for consumers. Conversely, a stronger domestic currency may make imports more affordable but can harm domestic industries reliant on exports.
Mitigating Volatility:
Governments and central banks often intervene to stabilize currency markets during periods of excessive volatility. They may use measures such as capital controls, interest rate adjustments, or direct market interventions to influence exchange rates. However, these interventions are not always foolproof and can have unintended consequences.
Conclusion:
Volatility in currency markets due to speculation and political uncertainty is a significant con of the global economy. It poses challenges for businesses, investors, and consumers alike. While some level of volatility is inevitable, efforts should be made to promote stability and transparency in currency markets through prudent economic policies and effective risk management strategies. By addressing these concerns, we can strive for a more predictable and resilient global economy that benefits all stakeholders.
Vulnerability to global economic shocks, such as pandemics or natural disasters
Title: Vulnerability to Global Economic Shocks: Lessons Learned from Pandemics and Natural Disasters
Introduction:
The global economy is a powerful engine that drives growth, innovation, and prosperity. However, it is not without its vulnerabilities. One significant con of the global economy is its susceptibility to shocks that can disrupt entire systems and have far-reaching consequences. In this article, we will explore the vulnerability of the global economy to shocks such as pandemics and natural disasters.
Pandemics:
The recent COVID-19 pandemic serves as a stark reminder of how vulnerable the global economy can be to health crises. The rapid spread of the virus across borders resulted in widespread lockdowns, travel restrictions, and disruptions to supply chains. Industries such as tourism, hospitality, and aviation were severely impacted, leading to job losses and economic downturns.
Pandemics not only affect public health but also have significant economic implications. Governments worldwide had to implement stringent measures to contain the virus’s spread, which led to reduced consumer spending, business closures, and decreased investor confidence. The interconnectedness of economies meant that a shock in one country quickly reverberated throughout the global economic system.
Natural Disasters:
Natural disasters pose another threat to the global economy. Events like earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, or wildfires can cause immense destruction and disrupt critical infrastructure. These disasters often result in loss of life, displacement of communities, damage to businesses and homes, and significant economic setbacks.
When a natural disaster strikes a region heavily involved in global supply chains or production networks, it can lead to disruptions in manufacturing processes or delays in product deliveries. This can have cascading effects on industries around the world that rely on those supplies or components.
Lessons Learned:
The vulnerabilities exposed by pandemics and natural disasters highlight the need for resilience in our global economic systems. Governments and businesses must learn from these events and take proactive measures to mitigate future risks.
Investing in robust healthcare systems, early warning systems, and emergency response capabilities can help countries better manage health crises. Diversifying supply chains, creating redundancy in critical infrastructure, and implementing disaster risk reduction strategies can enhance resilience against natural disasters.
Collaboration and coordination between nations are crucial in times of crisis. Sharing information, expertise, and resources can help mitigate the impact of shocks on the global economy. International organizations play a vital role in facilitating cooperation and providing support during challenging times.
Conclusion:
While the global economy has brought immense benefits, it also faces vulnerabilities when confronted with shocks such as pandemics or natural disasters. Understanding these risks and taking proactive measures to build resilience is essential for safeguarding economies worldwide. By learning from past experiences and working together, we can create a more resilient global economic system that is better equipped to withstand future challenges.
Environmental degradation caused by unsustainable production practices
Title: Unsustainable Production Practices and the Environmental Toll on our Global Economy
Introduction:
While the global economy has brought immense progress and prosperity, it has also come at a significant cost to the environment. Unsustainable production practices, driven by profit-seeking motives and a lack of environmental consciousness, have led to severe environmental degradation. In this article, we will delve into this con of the global economy and its impact on our planet.
Overexploitation of Natural Resources:
One of the major consequences of unsustainable production practices is the overexploitation of natural resources. Industries such as mining, agriculture, and manufacturing often prioritize short-term gains over long-term sustainability. This has resulted in deforestation, depletion of freshwater sources, soil erosion, and loss of biodiversity. These activities disrupt ecosystems and threaten the delicate balance that supports life on Earth.
Pollution and Climate Change:
Unsustainable production practices contribute significantly to pollution and climate change. Industrial processes release harmful emissions into the atmosphere, leading to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. The burning of fossil fuels for energy generation is a major contributor to climate change, resulting in rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea-level rise, and other ecological imbalances.
Waste Generation:
The global economy’s emphasis on mass production and consumption has led to an alarming increase in waste generation. From plastic packaging to electronic waste, our planet is grappling with mountains of discarded materials that often end up in landfills or pollute our oceans. Improper waste management not only harms ecosystems but also poses health risks for humans and wildlife.
Threats to Human Health:
Environmental degradation caused by unsustainable production practices directly impacts human health. Air pollution leads to respiratory problems while water contamination affects access to clean drinking water. Additionally, exposure to hazardous chemicals used in industries can have long-term health implications for workers and communities residing near production facilities.
Loss of Ecosystem Services:
Ecosystems provide invaluable services such as clean air, water purification, pollination, and climate regulation. However, unsustainable production practices disrupt these services, leading to a loss of ecological balance. This not only affects biodiversity but also compromises the long-term sustainability of industries that rely on these ecosystem services.
Conclusion:
Environmental degradation caused by unsustainable production practices is a significant con of the global economy. It poses threats to our planet’s ecosystems, human health, and long-term economic viability. Addressing this challenge requires a shift towards sustainable production methods that prioritize environmental stewardship and resource efficiency. By adopting cleaner technologies, promoting circular economies, and implementing responsible regulations, we can mitigate the environmental toll of our global economy and strive for a more sustainable future for all.